Here’s how a multi-spacecraft mission used a lunar gravity assist in 2009.
The moon’s gravity was utilized, in 2009, to change the trajectory of the Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite (LCROSS) mission, comprised of the (1) Centaur upper stage rocket, and the (2) Shepherding Spacecraft, launched together with another spacecraft, the companion (3) Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). All three were connected to each other for launch, but then the LRO separated one hour after launch.
The two LCROSS vehicles were slated to impact a lunar crater, in search for water. The LRO was slated to assume a lunar orbit for one year.
LCROSS Mission: Centaur upper stage rocket, and Shepherding Spacecraft positioning
On June 23, four and a half days after launch, LCROSS and its attached Centaur booster rocket successfully completed a lunar swingby and entered into polar Earth orbit with a period of 37 days, positioning LCROSS for impact on a lunar pole.
Source: Wikipedia on LCROSS
Image description: 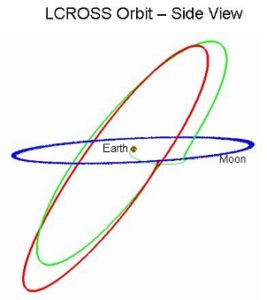
Image source: NASA, by Ohms law.
Lunar Reconaissance Orbiter (LRO) positioning
On June 23, 2009, the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter entered into orbit around the Moon after a four and a half day journey from the Earth. When launched, the spacecraft was aimed at a point ahead of the Moon’s position. A mid-course correction was required during the trip in order for the spacecraft to correctly enter Lunar orbit. Once the spacecraft reached the far side of the Moon, its rocket motor was fired in order for it to be captured by the Moon’s gravity into an elliptical lunar orbit.[30] A series of four rocket burns over the next four days put the satellite into its commissioning phase orbit where each instrument was brought online and tested. On September 15, 2009, the spacecraft started its primary mission by orbiting the Moon at about 50 kilometers (31 mi) for one year.
Source: Wikipedia on Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
Source: Here are some videos about the LCROSS and LRO missions.
How to plot an orbit
If you would like to have a go at finding or plotting possible orbits, try this resource:
For help explaining all of this, I turned to Mike Loucks of The Astrogator’s Guild. The Astrogator’s Guild uses a software package called STK/Astrogator from Analytical Graphics Inc. that is used to help spacecraft mission managers plan the trajectories of a variety of space missions. The software has been used on numerous NASA missions, including WMAP, LRO, LCROSS, New Horizons, Messenger, LADEE and MAVEN.
Source: How to get a satellite into geostationary orbit
Visit the next page to see this article’s Table of Contents.