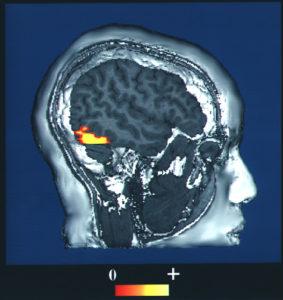
This is a computer-enhanced fMRI scan of a person who has been asked to look at faces. The image shows increased blood flow in the part of the visual cortex that recognizes faces.
What is the difference between an MRI and a Functional MRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging is generally used to evaluate the presence of hydrogen within the body, to identify a disease process, whereas the Functional MRI is a tool for analyzing brain function. This difference in purpose is seen in the targeted condition of cells being analyzed. At differencebetween.net, the difference is described thusly:
. . . . the measurement of signals is different for an MRI and an fMRI individually. An MRI studies the water molecule’s hydrogen nuclei whereas an fMRI calculates the levels of oxygen. In atomic physics, the MRI’s structural imaging views at a high resolution the difference between tissue types with respect to space. On the other hand, an fMRI’s functional imaging views the tissue differences with respect to time. In addition to this, an MRI has a high, spatial resolution while an fMRI has a long-distance, superior, temporal resolution.
Source: www.differencebetween.net
What is Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)?
Functional MRI (fMRI) is used to understand how different parts of the brain respond to external stimuli or passive activity in a resting state. Blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) fMRI measures the hemodynamic response to transient neural activity resulting from a change in the ratio of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin. Statistical methods are used to construct a 3D parametric map of the brain indicating those regions of the cortex which demonstrate a significant change in activity in response to the task. fMRI has applications in behavioral and cognitive research as well as in planning neurosurgery of eloquent brain areas.[28][29]
. . . .
Functional MRI (fMRI) measures signal changes in the brain that are due to changing neural activity. Compared to anatomical T1 [Weighted] imaging, the brain is scanned at lower spatial resolution but at a higher temporal resolution (typically once every 2–3 seconds). Increases in neural activity cause changes in the MR signal via T2* changes;[145] this mechanism is referred to as the BOLD (blood-oxygen-level dependent) effect. Increased neural activity causes an increased demand for oxygen, and the vascular system actually overcompensates for this, increasing the amount of oxygenated hemoglobin relative to deoxygenated hemoglobin. Because deoxygenated hemoglobin attenuates the MR signal, the vascular response leads to a signal increase that is related to the neural activity. The precise nature of the relationship between neural activity and the BOLD signal is a subject of current research. The BOLD effect also allows for the generation of high resolution 3D maps of the venous vasculature within neural tissue.While BOLD signal analysis is the most common method employed for neuroscience studies in human subjects, the flexible nature of MR imaging provides means to sensitize the signal to other aspects of the blood supply. Alternative techniques employ arterial spin labeling (ASL) or weighting the MRI signal by cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV). The CBV method requires injection of a class of MRI contrast agents that are now in human clinical trials. Because this method has been shown to be far more sensitive than the BOLD technique in preclinical studies, it may potentially expand the role of fMRI in clinical applications. The CBF method provides more quantitative information than the BOLD signal, albeit at a significant loss of detection sensitivity.[citation needed]
For more in-depth discussion see the source article at wikipedia.org.
Image source: Wikimedia Commons
To see how a voxel is utlized in an MRI, visit the next page.